Tulum Mayan Ruins
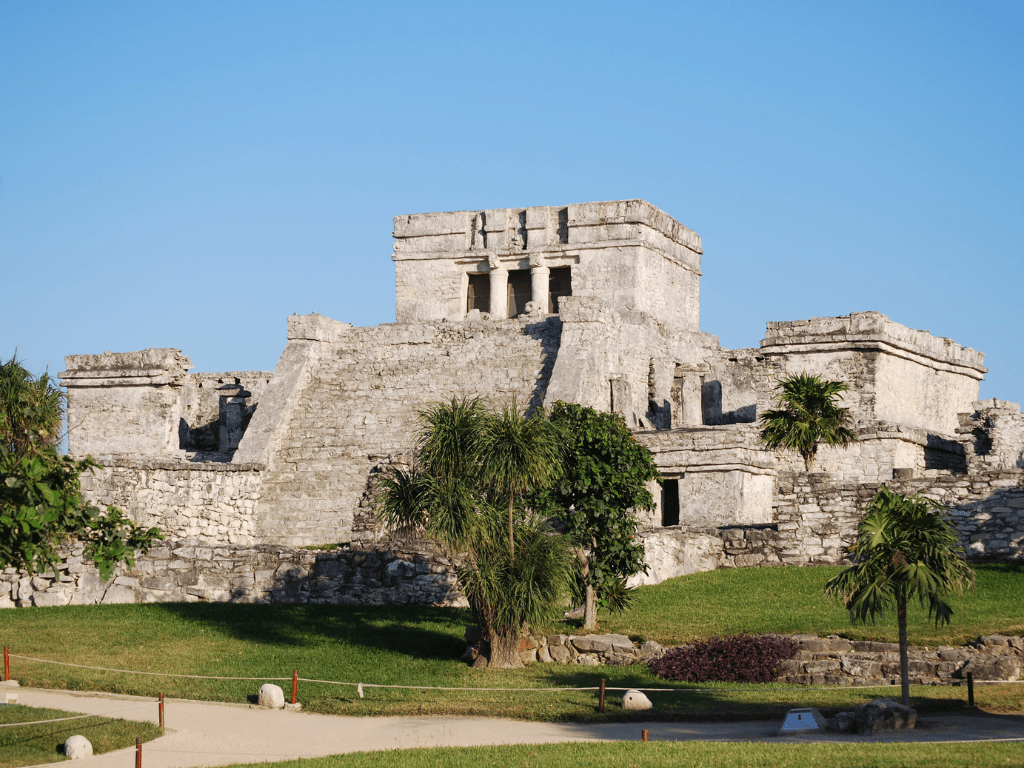

Introduction
Tulum ruins are some of the most well-preserved Mayan ruins in Mexico. The site is located on the east coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, overlooking the Caribbean Sea.
Tulum, meaning “wall” in Mayan, is believed to have been a major hub of trade and commerce during the height of Mayan civilization. The ruins are estimated to have been constructed between the years 1200 and 1450 AD, and were later abandoned by the end of the 16th century.
Brief history of Tulum ruins
The history of Tulum ruins dates back to the late Postclassic period, which spanned from 1200 to 1600 AD. During this time, Tulum was a significant trading port for jade and obsidian obtained from inland regions like Coba and Chichen Itza. The city was also important for its strategic location along ancient trade routes that connected Mesoamerican cultures with other parts of Mexico and Central America.
By around 1500 AD, Tulum had become an important political center within Mayan civilization. However, by the time Spanish explorers arrived in Mexico in the early 16th century, much of its former glory had already faded away.
Importance of Tulum ruins in Mayan civilization
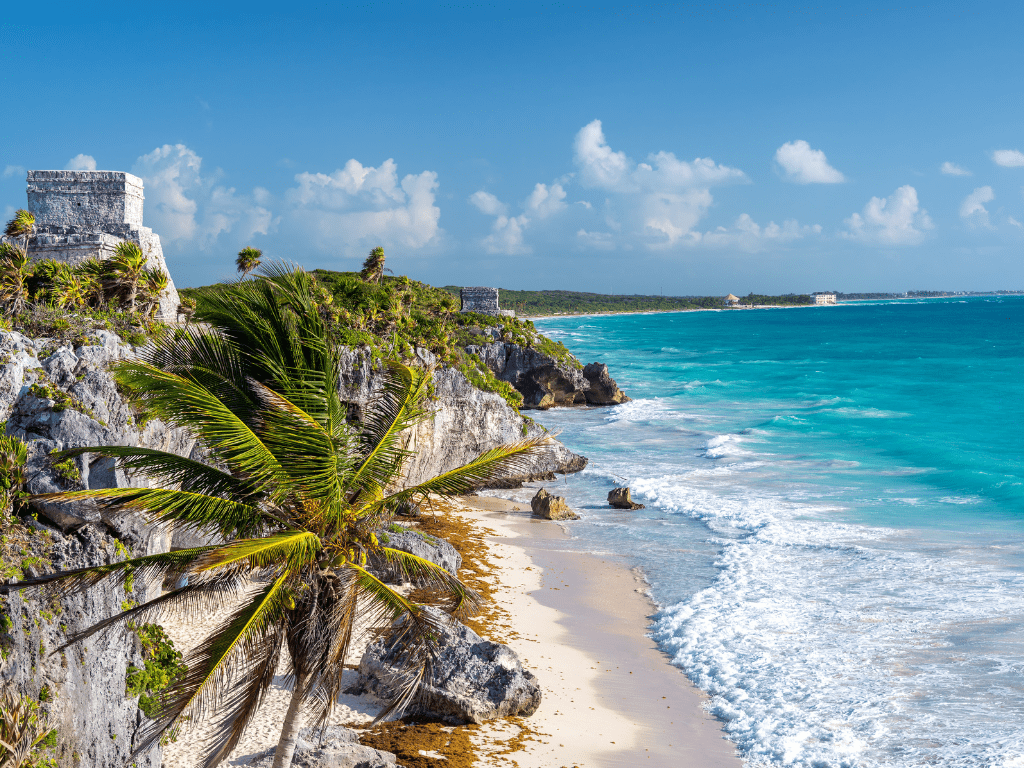

Despite its relatively small size compared to other ancient Mayan cities like Tikal or Palenque, Tulum held significant cultural importance during its heyday. Its location on a cliff overlooking turquoise waters made it an iconic symbol for ancient Maya culture that still captivates visitors today.
Historians also believe that Tulum played an important role in facilitating trade between Mesoamerican cultures like Toltecs and Aztecs as well as South American cultures like Incas. Archaeological findings suggest that Tulum played a key role in managing maritime trade routes in the area.
Understanding Tulum’s cultural significance is critical to understanding ancient Mayan civilization. Its well-preserved ruins offer a glimpse into how people lived during one of the most fascinating periods in human history.
Overview of Tulum Ruins
Geographic location and setting
Tulum ruins are located in the Yucatan Peninsula in the state of Quintana Roo, Mexico. The site is situated on a cliff facing the Caribbean Sea and is surrounded by a thick jungle that was once home to the ancient Maya civilization. The ruins themselves cover an area of about 39 acres and include numerous structures such as temples, palaces, and observatories.
Architectural style and design
The architectural style at Tulum is unique compared to other Mayan sites in Mexico. The buildings are characterized by their small size, lack of decoration, and low height – all features which are thought to have been influenced by military considerations.
The structures were built using limestone blocks and mortar made from burnt seashells. The roofs were made from wood and palm leaves.
Significance of the structures
The structures at Tulum have significant historical value because they provide insight into the culture and way of life of the ancient Maya people who inhabited this region over a thousand years ago. They also demonstrate advanced astronomical knowledge that helped them build their civilization around natural phenomena such as solstices or equinoxes. Additionally, Tulum was an important trade center for goods such as jade, obsidian, feathers, salt, honey – positioned right on top of a coastal highway that linked Mesoamerica with Central America.
Exploration of the Ruins
The Temple of the Frescoes
The Temple of the Frescoes is one of the most important structures in Tulum ruins. Built in the 13th century, it was used as a place for worship and observance of astronomical events.
The temple gets its name from the beautifully preserved frescoes that adorn its walls, depicting various scenes from Mayan life and mythology. One particularly striking image is that of Chaac, the Mayan god of rain, depicted with his characteristic lightning bolt scepter.
The frescoes were used to communicate religious beliefs and cultural practices to both worshippers and visitors. Unique features of this structure include its location atop a high platform overlooking the sea, which would have provided an unobstructed view for astronomical observations.
In addition, the temple has two rooms with intricate carvings on their doorways. Historical context reveals that this temple was built during a time when Tulum was experiencing significant growth and power as a trading center in Mayan civilization.
The Castle
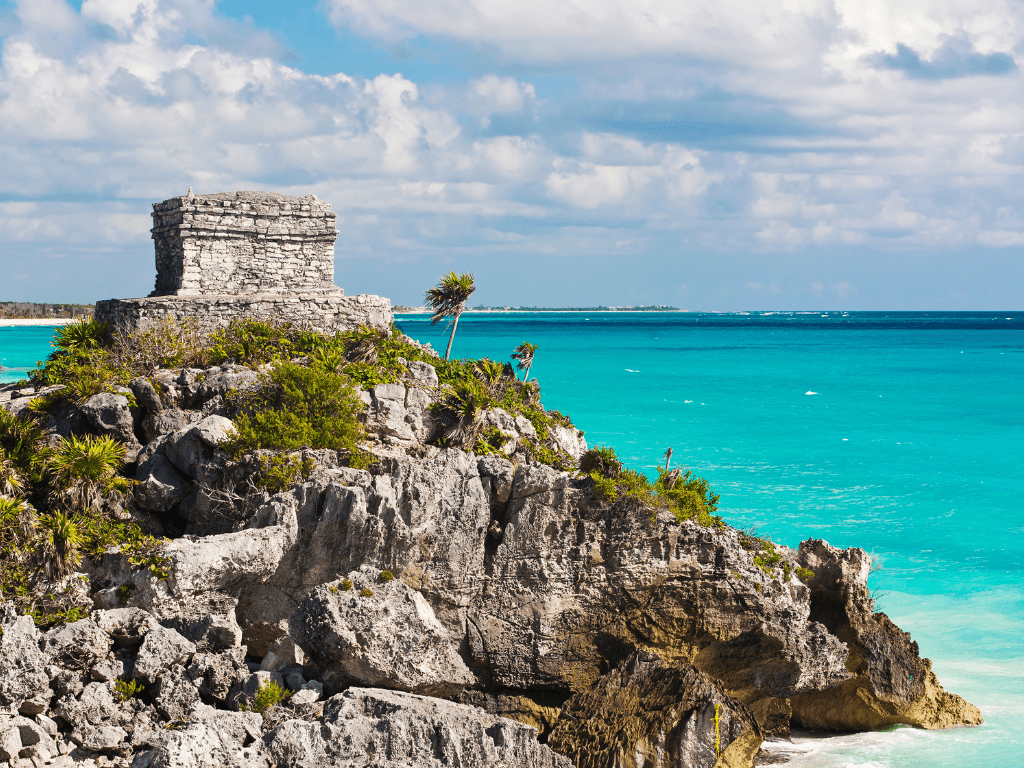
The Castle serves as both a defensive structure and an observation point at Tulum ruins. It was built on top of a cliff overlooking the Caribbean Sea and served as a lookout post for incoming ships while also providing protection against possible attackers from inland areas. One unique feature is its cylindrical shape which allowed defenders to fire arrows or throw objects in any direction without having to move around much.
Another significant feature is its location right next to El Castillo beach- said to be one of Mexico’s best beaches – making it easy for Mayans traveling by water to access it directly. Historical context reveals that this structure was built during Tulum’s peak period as a trade center in Maya civilization around 1200 AD.
The Wall
The Wall surrounds nearly all sides of Tulum ruins and serves as a defensive barrier against enemies. It is made up of limestone blocks, which are well-preserved and still standing strong today. One unique feature of this wall was that it had five openings or gates which lead to the ocean and inland areas, allowing for convenient trade routes.
The wall itself was built in a curved shape to offer maximum defense from attacks. Historical context reveals that this structure was built around the 13th century AD, during which Tulum became an important commercial center for trade in the region.
Exploring the ruins of Tulum leads to an understanding of the rich Mayan history and culture. The Temple of Frescoes, Castle and Wall are three prime examples of significant structures at Tulum ruins that have stood the test of time and continue to educate visitors about Mayan civilization.
Cultural Significance of Tulum Ruins
Mayan beliefs and practices at Tulum ruins
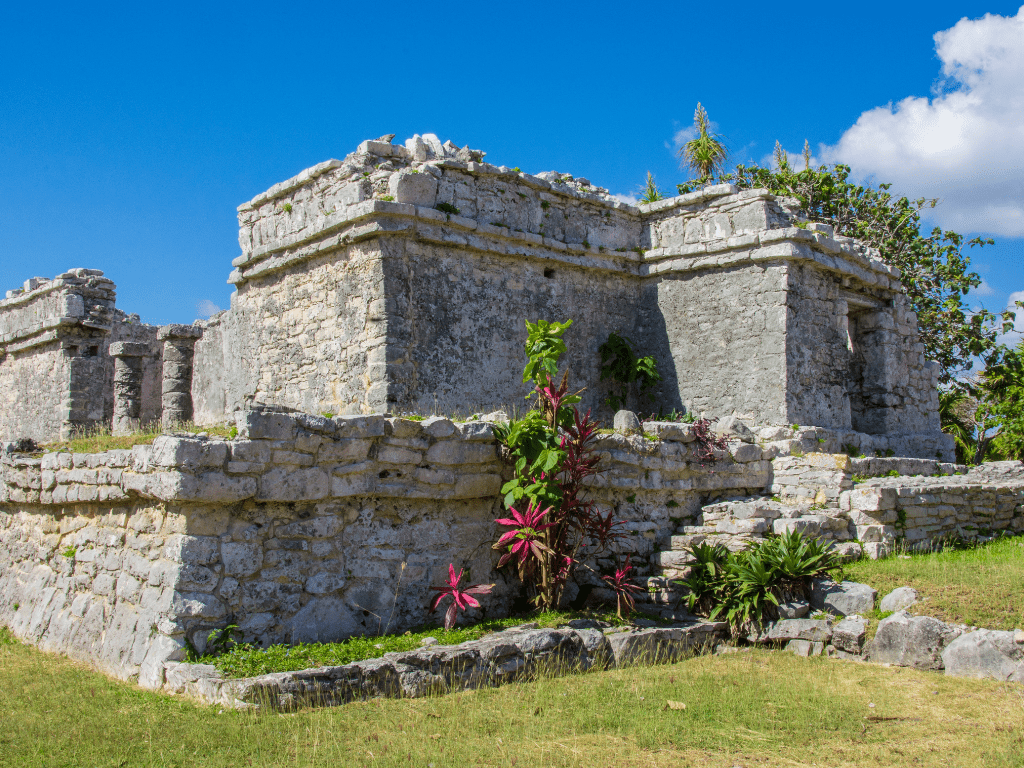
Tulum ruins hold significant cultural value as they are believed to have served as a Mayan trading hub during the Late Postclassic period. The Mayans who lived in Tulum believed that their city was the gateway between the spiritual and earthly worlds.
For this reason, they constructed several structures with intricate carvings and murals depicting their gods and goddesses, including Chaac – the god of rain, Chac Chel – the goddess of fertility, and Itzamna – the god of creation. Mayans also used Tulum ruins for religious ceremonies to honor their gods.
The ruins have evidence of sacrificial rituals which were performed to appease their gods. Offerings such as pottery, obsidian blades, jadeite jewelry, and other valuable items were also found in the tombs within the site.
Role of Tulum in trade and commerce during Mayan civilization
Tulum’s strategic location on a cliff overlooking the Caribbean Sea made it an essential trading center for seafaring merchants during its heyday. The Mayans traded goods like jadeite, obsidian blades, animal skins, honey, and cacao beans with neighboring cities like Xcaret and Cozumel.
With its location near maritime trade routes along Mexico’s coastlines between modern-day Belize and Honduras alongside its proximity to inland Maya territories where crops such as maize were grown; Tulum became one of the most important trading centers for ancient Maya culture. Tulum ruins not only showcase Mayan architectural ingenuity but also represent a significant cultural landmark for understanding pre-Columbian America’s history.
Preservation Efforts for Tulum Ruins
Current State of Preservation Efforts
The Tulum ruins have been subject to numerous preservation efforts over the years, with a focus on maintaining the integrity of the structures and protecting them from further damage. The National Institute of Anthropology and History has taken on a significant role in the preservation efforts by conducting regular maintenance work on the ruins, as well as monitoring their condition.
The site is also protected by various regulations that prohibit destructive activities such as digging or graffiti. However, despite these measures, there are still concerns about the state of preservation at Tulum.
The constant influx of tourists can cause wear and tear on the structures, while natural elements such as wind and rain can also take their toll. Additionally, climate change poses a new threat to the ruins, with rising sea levels potentially impacting their stability.
Challenges Faced in Preserving the Ruins
The challenges facing those tasked with preserving Tulum are many and varied. One of the biggest obstacles is ensuring that visitors to the site do not inadvertently cause damage through their actions – whether intentional or otherwise. To combat this problem, authorities have implemented strict rules surrounding visitor behavior; for example, tourists are no longer allowed to climb on any of the structures.
Another challenge comes from illegal activity around Tulum’s borders. In recent years there has been an increase in looting around archaeological sites across Mexico, which puts pressure on law enforcement officials to ensure that valuable artifacts do not fall into private hands.
There are also concerns about illegal construction near Tulum which may be impacting both its physical and cultural landscape. There is always a risk that natural disasters could impact Tulum’s fragile structures; for example hurricanes can cause significant damage to archaeological sites in coastal areas like Tulum.
Despite these challenges however there is hope for sustaining this historical wonder and preserving it for future generations. Through education, awareness, and commitment there is a possibility of protecting Tulum’s unique beauty for many years to come.
Conclusion:
Summary of key points discussed
The Tulum ruins are a significant historical site that boasts a rich history and culture. From its geographic location to its architectural design, Tulum stands out as a unique example of Mayan civilization. Some of the most notable structures include the Temple of the Frescoes, The Castle, and The Wall.
Each of these structures holds immense significance in Mayan religion and trade. We also explored the various cultural practices and beliefs that were practiced at Tulum ruins.
It is evident that this was an important hub for commerce and trade during Mayan civilization. The site’s preservation is vital in keeping it alive for future generations to experience firsthand.
Importance of preserving historical sites like Tulum ruins for future generations
Preserving historical sites like Tulum Ruins is essential because it allows us to connect with our past and understand our cultural heritage better. These sites offer an opportunity to learn about ancient civilizations’ ways of life, their accomplishments, traditions, rituals, architecture, art, and more.
In other words, they are essential in helping us understand where we come from. If we don’t preserve these sites now or educate people on their importance now, then they could disappear forever over time.
Future generations would miss out on experiencing them first hand or even learning about them through books or other forms of media. It’s not just about preserving structures; it’s also about preserving stories – stories that create a sense of identity and belonging for all cultures globally.
As such, there must be dedicated efforts in place to ensure that these historical sites remain intact for many generations to come while still allowing visitors to interact with them safely. Doing so will enable visitors to experience the beauty of Tulum ruins while still protecting it from further damage or destruction due to human activities such as tourism development or climate change impacts.
In closing, preserving Tulum ruins is not only a cultural duty but a moral one. It serves as an opportunity for all of us to learn from the past and appreciate our shared heritage. Please keep in mind the Yucatan is scattered with Mayan ruins. Check out our list of the 8 most important Mayan ruins.


