Exploring the Wonders of Edzna Mayan Ruins
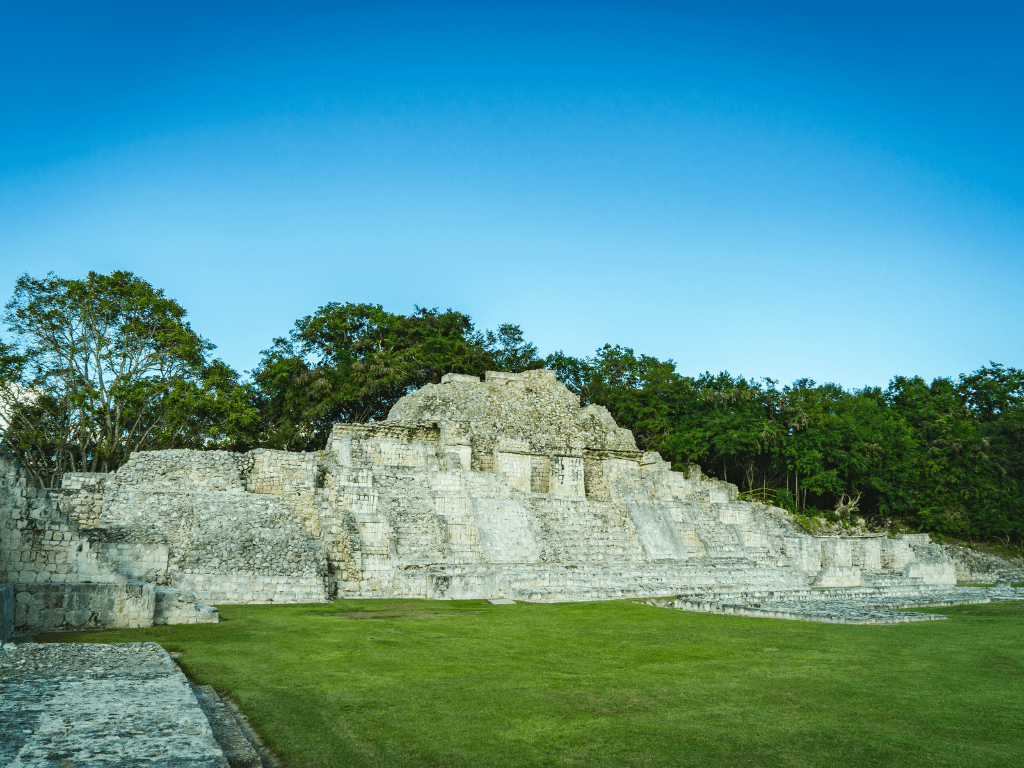

Edzna is a magnificent archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Campeche, approximately 50 kilometers southeast of the city of Campeche. The name “Edzna” means “house of the Itzaes,” referring to one of the most important Mayan ethnic groups that lived in this region from around AD 600 to AD 1450. This ancient city is believed to have been inhabited continuously for over a thousand years and was one of the most important political and religious centers within the Mayan civilization.
The Importance of Edzna in the Mayan Civilization
The Mayan civilization was one of the oldest and most advanced civilizations in Mesoamerica, with significant achievements in art, architecture, astronomy, mathematics, and writing systems. The people who lived at Edzna were part of a larger network of cities spread throughout Central America that shared cultural similarities but also had their unique characteristics.
Edzna played an essential role in this network as it served as a political and religious center for many smaller settlements around it. This ancient city was considered one among few cities that maintained political control over its surrounding regions while also being an important hub for trade routes due to its proximity to coastal regions.
Brief Overview: A Walkthrough through Edzna Mayan Ruins
Visitors approaching Edzna will be greeted by towering pyramids, impressive plazas, ball courts and monumental palaces surrounded by lush tropical vegetation. The site’s complex architectural layout spans about two square kilometers with more than 100 structures identified so far.
Visitors can explore different parts of Edzna’s urban complex through several paths highlighting various features such as:
The Main Plaza – this is the central hub of the ancient city, and it features many important structures, including the Great Acropolis, which is a pyramid with ten tiers and offers panoramic views of the surrounding terrain.
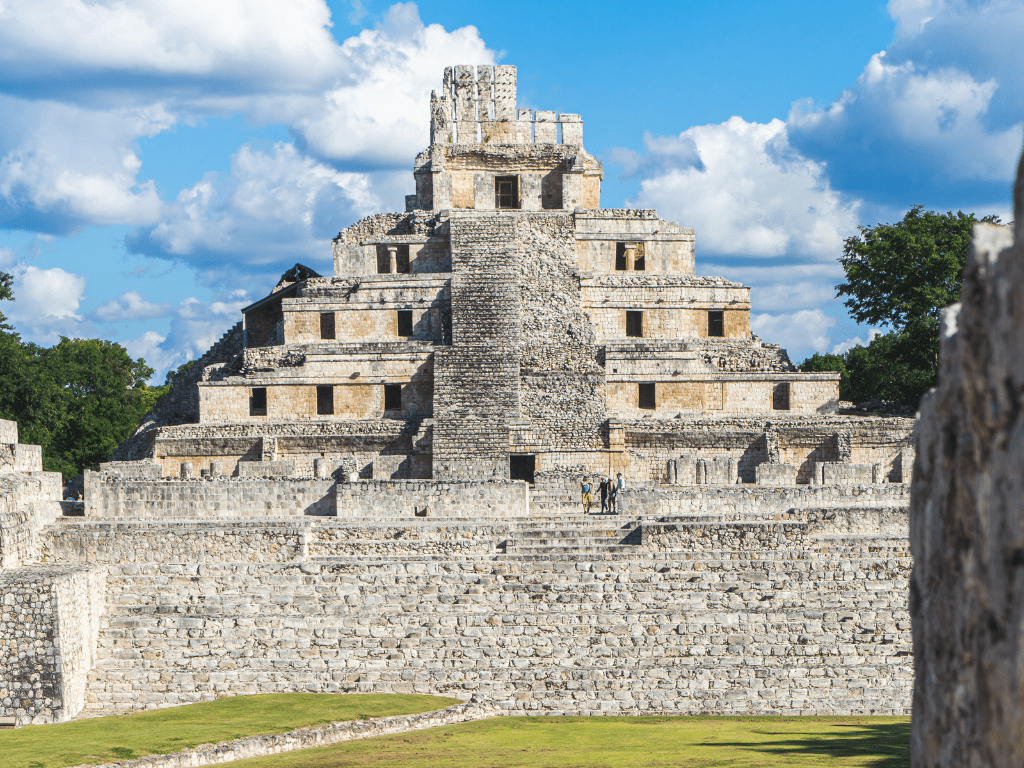
The Temple of Five Stories – located towards the eastern part of the site, this beautiful stepped pyramid has five levels with a shrine on top.
The Ball Court – located in the northern part of Edzna, is one of the largest ball courts in Mayan civilization.
History and Background of Edzna Mayan Ruins

Location and Geographical Features
Edzna is a Maya archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Campeche, approximately 50 km southeast of the city of Campeche. The site is situated on a limestone plateau that rises above the surrounding forest, providing an impressive panoramic view of the area.
The plateau is surrounded by swamps and low-lying areas, which may have served as an important source of freshwater. Edzna covers an area of approximately 25 square km.
Historical Timeline of the Site
The earliest evidence of occupation at Edzna dates back to around 400 BC. The city reached its peak during the Late Classic period (600-900 AD), when it was one of the most important political and ceremonial centers in the region. At its height, Edzna had a population estimated at between 25,000 and 30,000 people. However, by around 1200 AD, the city had been abandoned.
Significance of the Name “Edzna”
The name “Edzna” comes from the Yucatec Mayan language and means “house or place where something is repeatedly done.” This likely refers to some kind of ritual or ceremony that was regularly performed at this site. It is believed that this name was given to this ancient site by later Mayan peoples who visited or settled in this region after its original inhabitants had left it abandoned
Architecture and Design of Edzna Mayan Ruins

Overview of the layout and design
Edzna is a classic example of the Mayan architectural style. Its unique design can be traced back to the early period of Mayan civilization.
The city was built on a series of leveled terraces with a centralized core area that included clusters of structures and open plazas. The core area, which is the most prominent part of Edzna, features towering pyramids, temples, palaces, residences, and ball courts.
Notable structures
The Great Acropolis is one of the most recognizable structures in Edzna. It stands 120 feet high and consists of a set of stairs that lead to a small temple at its peak.
On top stands an imposing structure used for religious ceremonies that provided panoramic views over the entire city. Another notable structure is the Temple of Five Stories (El Templo de los Cinco Pisos), which has five levels each connected by a steep stairway leading to its roof peak.
This temple was also used for religious ceremonies and provides breathtaking views in all directions. The Ballcourt was an important place for various social events in Edzna; it had seating platforms on both sides while players would throw rubber balls through hoops using their hips.
Unique architectural features
One notable feature is Edzna’s hydraulic system which highlights Mayan engineering skills. It includes several channels that run throughout the site connecting to large reservoirs used for collecting rainwater during rainy seasons; this water was then distributed across various areas during dry seasons as needed. Another unique feature is the use of stucco masks representing human faces on many buildings’ exteriors; these masks were often decorated with brightly colored pigments & symbolism reflecting certain beliefs or mythological concepts in Mayan culture such as the sun, moon, and gods.
Daily Life in Edzna Mayan Ruins

Social Structure and Hierarchy within the Community
The social structure of the Edzna Mayan Ruins was highly hierarchical. The nobles held the highest social status and were responsible for governing the city, maintaining its infrastructure, and organizing religious ceremonies. They lived in large palaces located within the Great Acropolis and enjoyed a luxurious lifestyle with many servants.
Below them were the commoners, who were primarily involved in agriculture and the production of goods such as textiles, pottery, and jewelry. They lived in smaller houses scattered throughout the city and often worked together to complete tasks such as building irrigation systems or constructing public buildings.
Agriculture and Farming Practices
The agricultural practices of the Edzna Maya Ruins were highly advanced for their time period. They used a combination of raised fields and irrigation canals to grow crops such as maize, beans, squash, chili peppers, and cotton. The raised fields allowed for better drainage during heavy rainfall while also increasing soil fertility by trapping organic matter.
The farmers also practiced crop rotation to preserve soil quality by alternating between different types of crops each year. Additionally, they used a complex system of terraces to farm on steep slopes that would have been otherwise unusable.
Religious Beliefs and Practices
Religion played a significant role in daily life at Edzna Maya Ruins as it did throughout all Mayan cities. The people worshiped a pantheon of gods who were believed to control various aspects of nature such as rain or fertility.
The rulers played an important role in religious ceremonies by performing rituals designed to maintain harmony between humans and gods. This included bloodletting ceremonies where they would pierce their tongues or genitals using stingray spines or obsidian knives to offer their blood as a sacrifice.
The people also believed in an afterlife and often included offerings of food, drink, and personal possessions in their tombs to ensure a successful journey to the underworld. These offerings have provided valuable insights into their daily lives and religious beliefs.
Decline and Abandonment of Edzna Mayan Ruins
Edzna was a significant city in the Mayan civilization from the early preclassic period, around 400 BC, to the late post-classic period, until around 1450 AD. However, by the time Spanish conquistadors arrived in Mexico during the 16th century, the site had been abandoned for centuries. There is no one theory as to why this happened; instead, scholars and archaeologists have proposed several possibilities.
Theories on why the city was abandoned
One theory is that Edzna suffered from environmental degradation due to deforestation and erosion caused by agricultural practices. This could have led to soil exhaustion and water shortages that made it difficult for inhabitants to sustain themselves.
Another theory is that a social or political crisis occurred within the city. This could have been a result of internal conflicts between different groups or a response to external pressures such as invasion or disease.
Evidence found at the site to support these theories
Archaeological evidence supports both theories mentioned above. For example, excavations at Edzna revealed evidence of intensive agricultural practices such as terracing and canal building.
These agricultural methods would have required significant amounts of labor and resources but could also have contributed to environmental degradation if not managed correctly. Additionally, researchers found many artifacts related to warfare scattered throughout the site.
Preservation Efforts for Edzna Mayan Ruins
Despite being abandoned for centuries, Edzna’s structures remained largely intact due to their unique architectural features – they were built with limestone blocks instead of adobe bricks like many other structures in Mesoamerica – as well as their remote location deep within the jungle.
Current state of preservation efforts for the ruins
Today, there are ongoing efforts by Mexican authorities and conservation groups to preserve the site and protect it from further deterioration. In 2012, Edzna was added to the World Monuments Fund’s Watch List of endangered sites due to concerns about illegal logging, agricultural encroachment, and tourism development.
Challenges faced in preserving a site like this
Preserving a site like Edzna is challenging due to its remote location and lack of resources. Proper maintenance requires not only regular cleaning but also significant funding for repairs, security measures, and archaeological research.
Future plans for preservation
Despite these challenges, there are ambitious plans underway to preserve Edzna for future generations. Proposed preservation measures include constructing visitor centers outside the ruins, introducing sustainable tourism practices that reduce impact on the site’s fragile environment, and increasing public outreach and education efforts.
Conclusion
Edzna Mayan Ruins remains an important cultural heritage site that provides valuable insight into the history of the Mayan civilization. While there is still much to learn about why this city was abandoned so many centuries ago, efforts are underway to ensure that its unique architectural features and historical significance are preserved for future generations. By working together to protect these ancient ruins through innovative conservation practices, we can ensure that they continue to inspire wonder in people around the world. Please keep in mind the Yucatan is scattered with Mayan ruins. Check out our list of the 8 most important Mayan ruins.